How To Search Google Scholar For Systematic Review
This is a protocol.
How to search google scholar for systematic review. Optimal searches in systematic reviews should search at least Embase MEDLINE Web of Science and Google Scholar as a minimum requirement to guarantee adequate and efficient coverage. Within systematic reviews when searching for relevant references it is advisable to use multiple databases. Embase MEDLINE including Epub ahead of print Web of Science Core Collection and Google Scholar.
To ensure adequate performance in searches ie recall precision and number needed to read we find that literature searches for a systematic review should at minimum be performed in the combination of the following four databases. Articles theses books abstracts and court opinions. Both subject headings and keyword searching in the databases that allow this and searching multiple databases where articles may be indexed differently or a very similar search.
We conclude that whilst Google Scholar can find much grey literature and specific known studies it should not be used alone for systematic review searches. We take seriously this concern. For more information on how to set up your Google Scholar Library click here.
For systematic reviews evidence-based reviews clinical practice guidelines. Monday I read the already infamous article published January 9th which concludes that Google Scholar is basically good enough to be used for systematic reviews without searching any other databases. Optimal searches in systematic reviews should search at least Embase MEDLINE Web of Science and Google Scholar as a minimum requirement to guarantee adequate and efficient coverage.
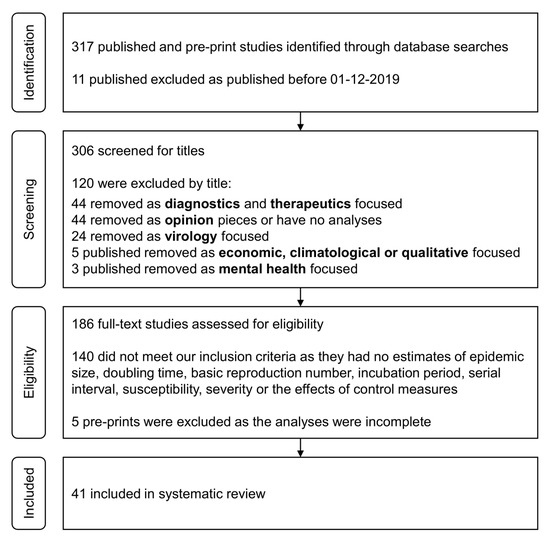
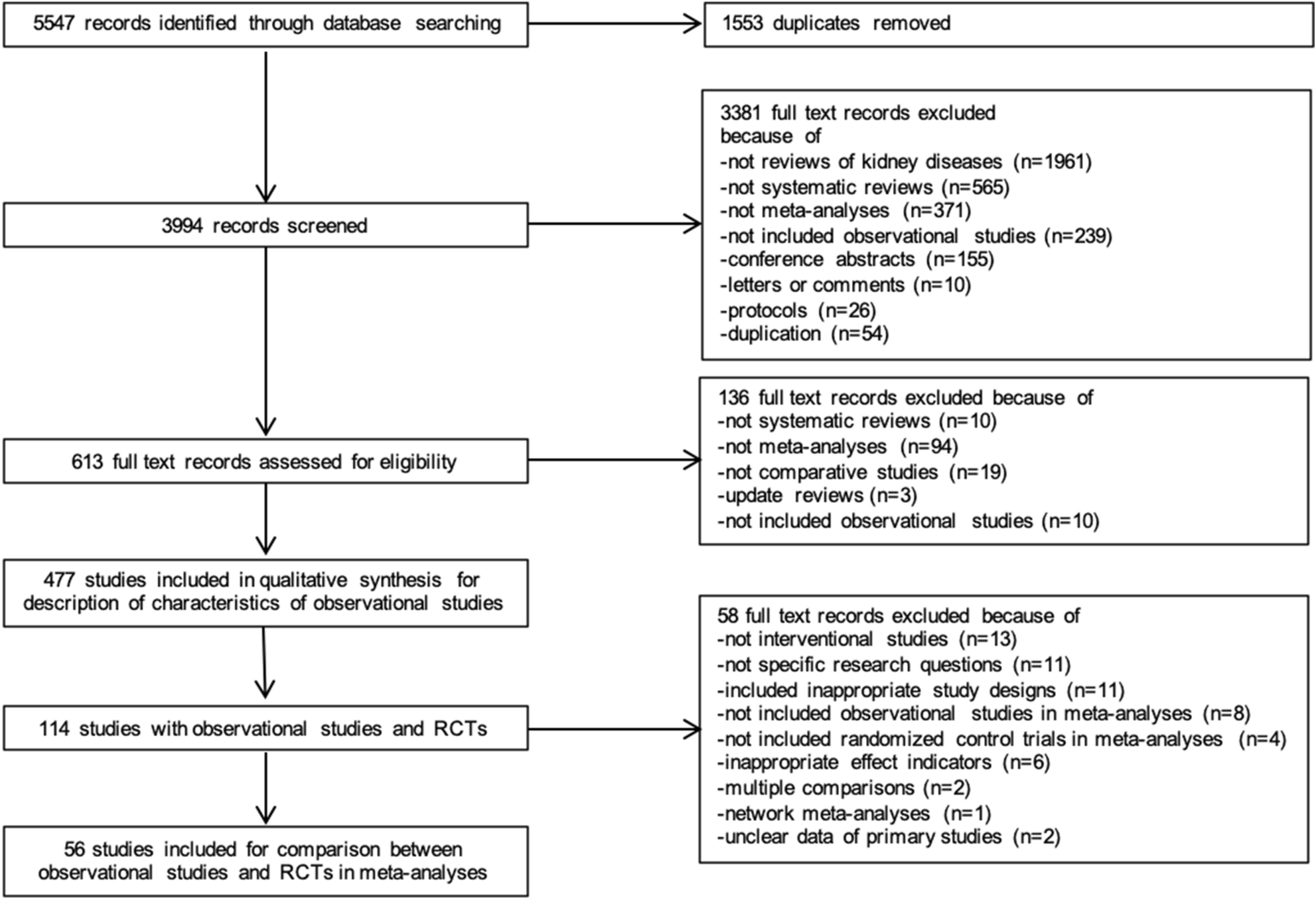
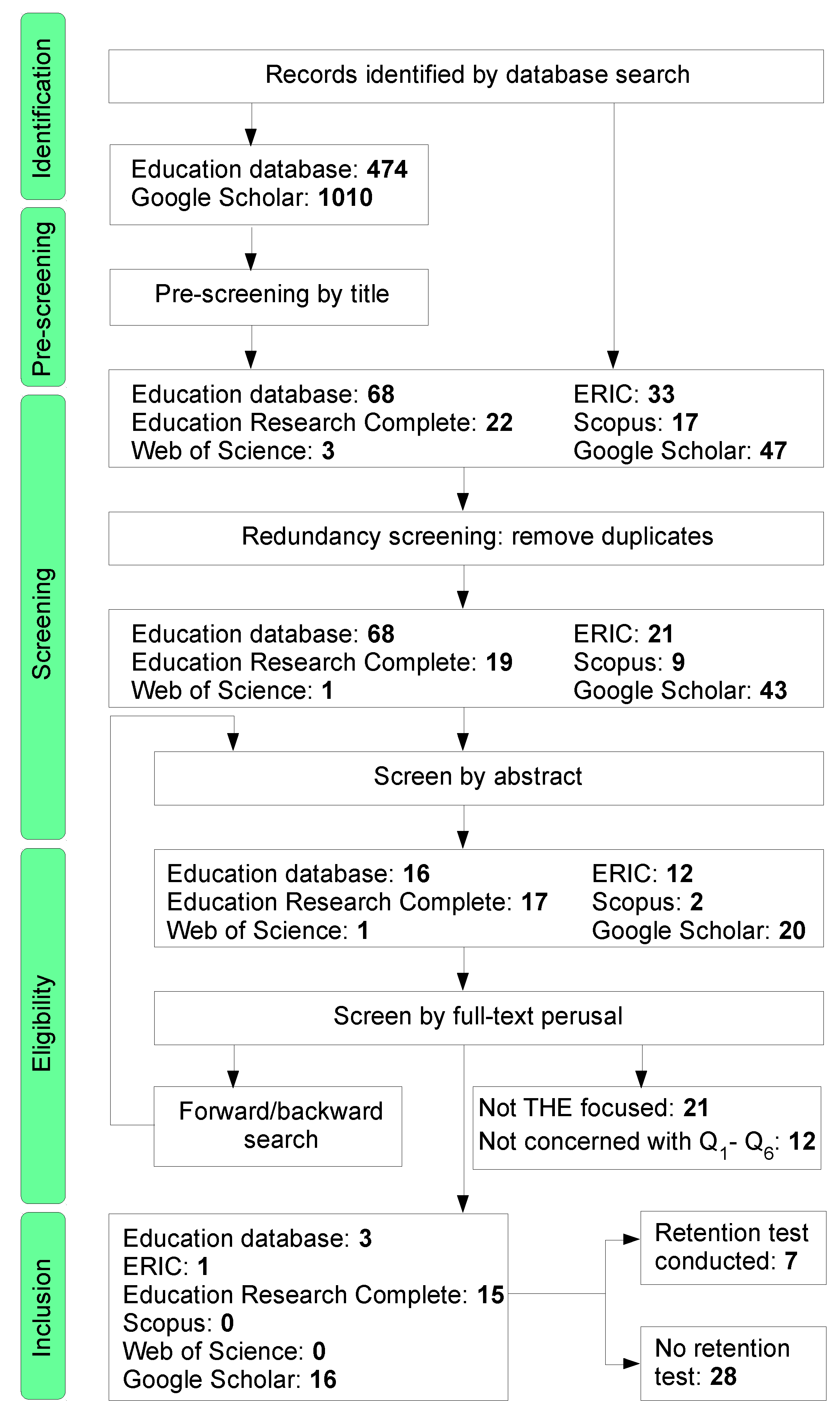
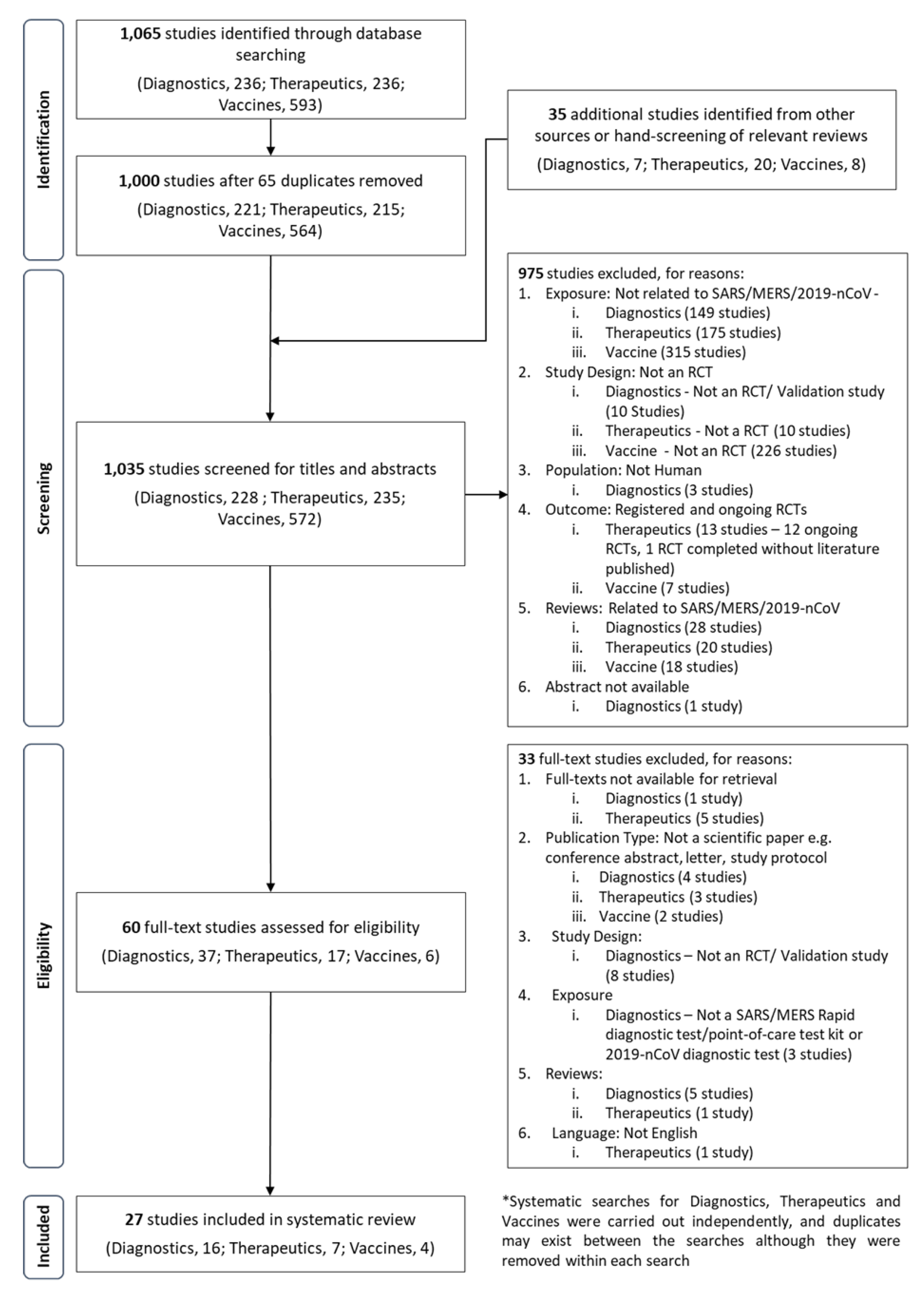
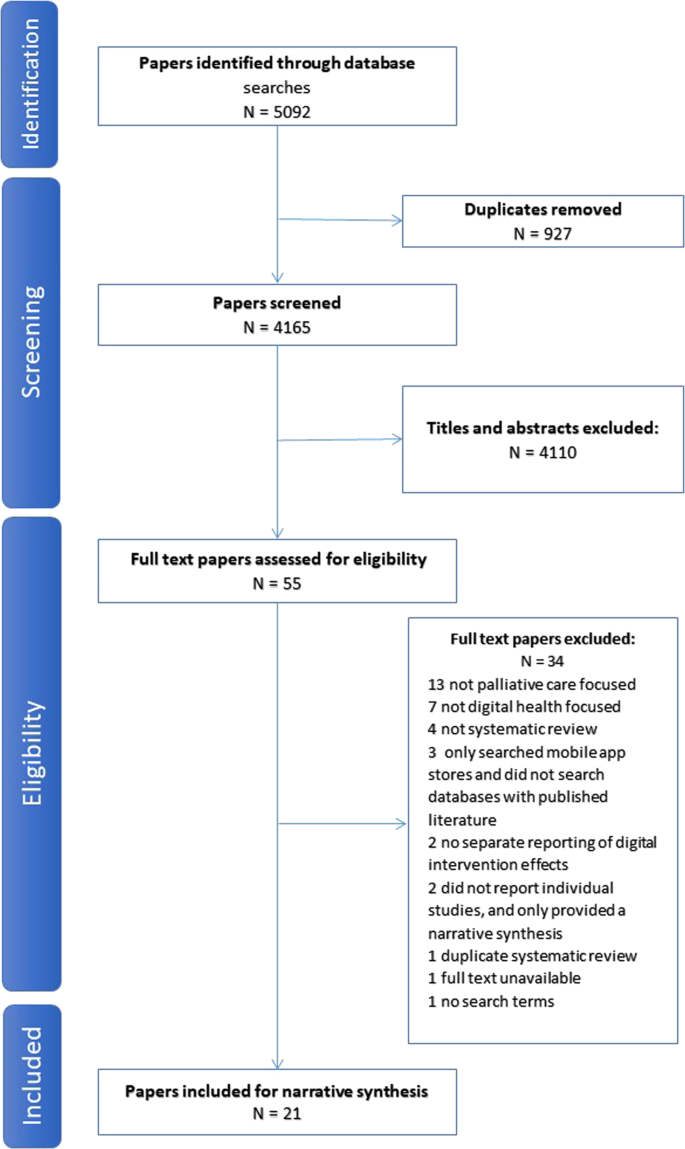
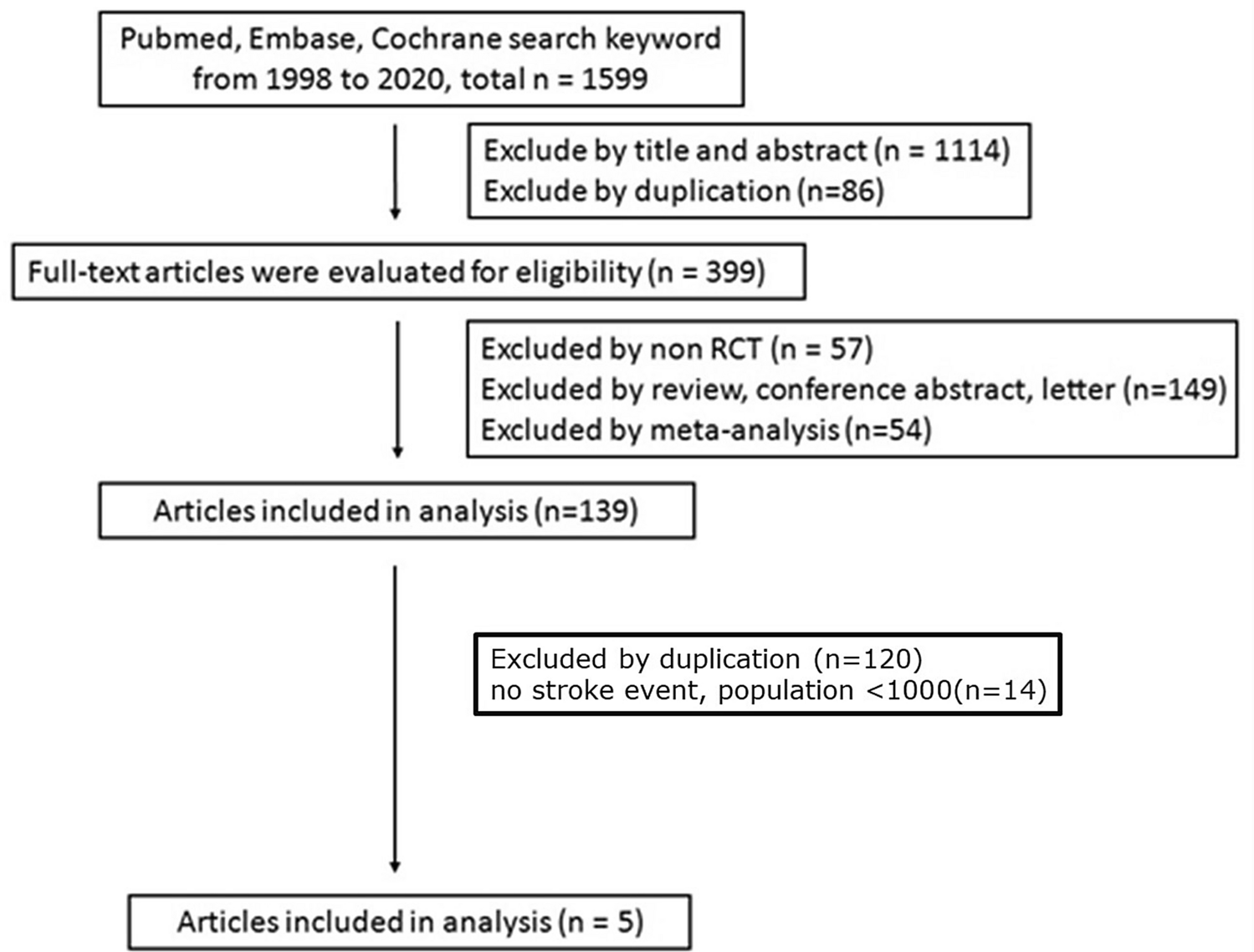
This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. Is Google Scholar enough to be used for systematic review searching. Systematic reviewmeta-analysis steps include development of research question and its validation forming criteria search strategy searching databases importing all results to a library and exporting to an excel sheet protocol writing and registration title and abstract screening full-text screening manual searching extracting data and assessing its quality data.
What approaches can we adopt to support effective systematic searching using Google Scholar. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically. Are not included in library databases eg some conference papers government reports articles from certain journals etc.